RAILWAY ENGINEERING
 |
| Railway engineering for transportation engineering |
Role of railways in transportation
E
conomic aspects
Cultural and Social aspects
Political aspects
Economical aspects :-
Due to
railways, the industrial development in for off places is possible, increasing the land values & standard of living of the people.
Also read :-plane table survey | easy to remember
Mobility of labour has contributed to industrial development.
During famines,
railways have played the vital role in transporting food & clothing to the affected areas.
Commercial farming is very much helped by the railway network throughout the country.
Speed movement of the commodities is possible through railways.
 |
| Railway engineering for transportation engineering |
Cultural & Social aspects :- Cultural & Social aspects :-
Railway has made it easier to reach places of religious importance.
Railway provide a convenient & safe mode of transport through out the country.
During travel as people of different caste & religions sit together the interaction is developed.
Political aspects :-
Railway have helped in the mass migration of the population.
Railway have created the sense of unity among the people of different religions, areas, castes & traditions.
With adequate network of railways, the central administration has become easy & effective.
 |
| Railway engineering for transportation engineering |
|
History of Railways in India
1832 :- First proposal for a railway in India, in between Madras(Now Chennai) & Bangalore. This remained a dream on paper.
1844 :- First proposal for the construction of railways, in India were submitted to East India company by Mr. R.Macdonald Stephenson.
1849 :- The construction of first experimental line of 160 kms from Calcutta to Mirzapur was undertaken by East India company.
1850 :- Contract to cons • 1853:- The first train in India was run at 3:30 PM on 16th April 1853, between Bombay & Thana. It carried about 400 people in 14 coaches & was driven by 3 engines.
1854:- On August 15th , the first passenger train in the Eastern railway section is operated, from Howarah to Hoogly (39kms).
1856 :- On July 1 st , the first train in the South railway was operated from Royapuram/(Madras) to Wallajah road (approx 100 kms) by the madras railway company.
1859 :- On March 3 rd , the first train in North railway was operated, from Allahabad to Kanpur (180kms).
1862 :- Feb-8 , Jamaipur Loco works establishes.
1864:- August 1 st , first train into Delhi.
1865:- Yamuna Bridge at Allahabad opened.
1869 :- Total track age in India is about 400 miles.
1870 :- Connectivity between Bombay & Calcutta. Mobile Post office services in train.
1879 :- India had a total of 14,920 kms of railway line.
1888 :- Construction of Bombay Victoria Terminus building is completed. Indian standard time (IST) comes into force for timekeeping in British India. 1905 :- Railway Board was established & Board is under the department of Commerce & Industry.
1915:- First over diesel locomotive in India.
1921:- The total length of line laid in India was 58,776kms.
• 1922 :-The railway board was reorganized.
• 1923 :- Nationalization of railway started. • 1936 :- Air conditioning Introduced in some (first class) passenger coaches.
• 1937 :- Burma was separated from India curtailing 3200 km line. 1942 :- Second world war ‘Military Transport Board’ was formed & for the movement of military line up to various strategic points.
• 1949-50 :- During that time most of the railway companies were acquired by the government. After Independence the following zonal grouping of railways was done in India.
Railway zones and headquarters
 |
| Railway engineering for transportation engineering |
|
Note:- It has recently been decided for better administration & management of Indian railways to set up following 16– new zones.(since from 2003)
Salient Features
Railway cover 63, 327 route Kms as on 2009
 |
| Railway engineering for transportation engineering |
|
Production Units:
 |
| Railway engineering for transportation engineering |
|
RAILWAY TRACK (PERMANENT WAY)
Definition :- The combination of rails, fitted on sleepers and resting on ballast & sub grade is called the railway track.
 |
| Railway engineering for transportation engineering |
|
Permanent way
• In a permanent way, the rails joined in series by fish plates & bolts and then they are fixed to sleepers by different types of fastenings. The sleepers properly spaced & boxed with ballast.
• The layers of ballast rest on the prepared sub grade called the formation.
 |
| Railway engineering for transportation engineering |
|
Fish Plates
 |
| Railway engineering for transportation engineering |
|
sleepers of railway
 |
| Railway engineering for transportation engineering |
|
Gauges
Definition :- It is the clear distance between two parallel rails laid.
 |
| Railway engineering for transportation engineering |
|
Gauges – Types
Standard Gauge -- UK, USA, Canada, Turkey, China 1435 mm (62%).
Broad Gauge -- India, Pakistan, Srilanka, Brazil, 1676 /1524 mm (15%) Argentina, Russia
Cape Gauge -- Africa, Japan, Australia, 1067 mm (8%) New Zealand
Meter Gauge -- India, France, Argentina, 1000 mm (9%) Switzerland
Other 23 in no’s -- Other countries
Gauges – In India
Broad Gauge (B.G) --- 1676 mm , 63% Route km.
Meter Gauge (M.G) --- 1000 mm, 31% Route km.
Narrow Gauge (N.G) --- 763 mm / 610 mm , 06% Route km.
Requirement of an ideal Permanent way
Requirement of an ideal permanent way so as to achieve high speed & better riding qualities with less future maintenance.
The gauge should be correct & uniform.
The rails should be in proper level. In a straight track, two rails must be at the same level.
The alignment should be correct, i.e should be free from kinks or irregularities.
The gradient should be uniform & as gentle as possible.
There should be adequate provisions for easy renewals & replacement
The track should be resilient & elastic in order to absorb shocks & vibrations of running track.
The radii & super elevation on curves should be properly designed & maintained.
Drainage system must be perfect for enhancing safety & durability of track.
The various components of the track, i.e the rails, fittings, sleepers, ballast& formation must fully satisfy the requirements for which they have been provided.
The track structure should be strong, low in initial cost as well as ,maintenance cost
Selection of Gauges
1) Cost of construction :-
• Land, components & earth work : Proportional Increases.
• Bridges etc : Marginal Increases.
• Buildings, Signals etc : No Increase.
2) Physical features of country:-
• Gradients
• Curves Narrow gauge is more suited to the above conditions. Eg:- Hill Railways :- Kalka – Shimla; Darjeeling ; Uttakmund (Ooty).
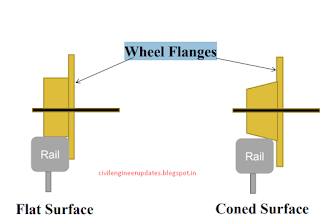
Coning of wheels
The distance between the inside edges of wheel flanges is generally kept less than the gauge of the track. So there is a gap between the wheel flanges and running edges of the rails, nearly equal to 1 cm (3/8”) on either side. Normally the tread of wheels is absolutely dead center of the head of the rail, as the wheel is coned to keep it in this central position automatically. These wheels are coned at a slope of 1 in 20.
 |
| Railway engineering for transportation engineering |
|
 |
| Railway engineering for transportation engineering |
|
Wheel Flanges
 |
| Railway engineering for transportation engineering |
|
There are two types
Flat Surface
Unequal moment on curved rails
Problems with flat wheel
Lateral sway on straight track, wearing of flanges & side of rail head.
Unequal moment on curved rails
Longer distance to be moved on outer curved rails as compared to inner curved rail.
 |
| Railway engineering for transportation engineering |
|
Advantages of coning of wheels
To reduce the wear & tear of the wheel flanges & rails, which is due to rubbing action of flanges with inside faces of the rail head. To provide a possibility of lateral movement of the axle with its wheels. To provide the wheels from slipping to some extent. Smooth riding.
Disadvantages of coning of wheels
Pressure on outer rail is more while on inner rail it is less. This results in wear of outer rail. If no base plate is used under the voids sleepers under the edge of the rail are damaged.