FLOW MEASURING DEVICES
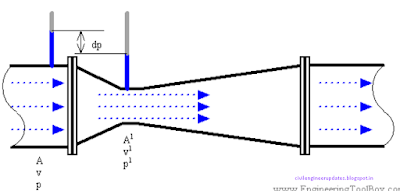
Venturi Tube
Due to simplicity and dependability, the Venturi tube flowmeter is often used in applications where it's necessary with higher Turn down rates, or lower pressure drops, than the orifice plate can provide. In the Venturi Tube the fluid flowrate is measured by reducing the cross sectional flow area in the flow path, generating a pressure difference. After the constricted area, the fluid is passes through a pressure recovery exit section, where up to 80% of the differential pressure generated at the constricted area, is recovered.
 |
| vanturi meter |
uses
With proper instrumentation and flow calibrating, the Venturi Tube flowrate can be reduced to about 10% of its full scale range with proper accuracy. This provides a turndown rate 10:1. Orifice, nozzle and Ventury meter.
Rotameter
The rotameter consists of a vertically oriented glass (or plastic) tube with a larger end at the top, and a metering float which is free to move within the tube. Fluid flow causes the float to rise in the tube as the upward pressure differential and buoyancy of the fluid overcome the effect of gravity. The float rises until the annular area between the float and tube increases sufficiently to allow a state of
dynamic equilibrium between the upward differential pressure and buoyancy factors, and downward gravity factors. The height of the float is an indication of the flow rate. The tube can be calibrated and graduated in appropriate flow units.
 |
| Rotamitre |
Uses
The rotameter meter typically have a TurnDown Ratio up to 12:1. The accuracy may be as good as 1% of full scale rating. Magnetic floats can be used for alarm and signal transmission functions.
Pitot Tube
The pitot tube are one the most used (and cheapest) ways to measure fluid flow, especially in air applications like ventilation and HVAC systems, even used in airplanes for speed measurent. The pitot tube measures the fluid flow velocity by converting the kinetic energy of the flow into potential energy. The use of the pitot tube is restricted to point measuring. With the "annubar", or multi-orifice pitot probe, the dynamic pressure can be measured across the velocity profile, and the annubar obtains an averaging effect.
Vortex flow meter
Principle of Vortex flowmeter - An introduction to the vortex flowmeter principle. • An obstruction in a fluid flow creates vortices in a downstream flow. Every obstruction has a critical fluid flow speed at which vortex shedding occurs. Vortex shedding is the instance where alternating low pressure zones are generated in the downstream.
 |
| vortex flow meter |
uses
These alternating low pressure zones cause the obstruction to move towards the low pressure zone. With sensors gauging the vortices the strength of the flow can be measured.
Calorimetric Flowmeter
The calorimetric principle for fluid flow measurement is based on two temperature sensors in close contact with the fluid but thermal insulated from each other. One of the two sensors is constantly heated and the cooling effect of the flowing fluid is used to monitor the flowrate. In a stationary (no flow) fluid condition there is a constant temperature difference between the two temperature sensors. When the fluid flow increases, heat energy is drawn from the heated sensor and the temperature difference between the sensors are reduced. The reduction is proportional to the flow rate of the fluid.
 |
| calorimetric flowmeter |
uses
Response times will vary due the thermal conductivity of the fluid. In general lower
thermal conductivity require higher velocity for proper measurement. The calorimetric flowmeter can achieve relatively high accuracy at low flow rates.
FLOW MEASURING DEVICES
Weirs
Weirs are structures consisting of an obstruction such as a dam or bulkhead placed across the open channel with a specially shaped opening or notch. The flow rate over a weir is a function of the head on the weir.
Common weir constructions are the rectangular weir, the triangular or v-notch weir, and the broad-crested weir. Weirs are called sharp-crested if their crests are constructed of thin metal plates, and broad-crested if they are made of wide timber or concrete.
 |
| weirs |
Orifice Plate
With an orifice plate, the
fluid flow is measured through the difference in pressure from the upstream side to the downstream side of a partially obstructed pipe. The plate obstructing the flow offers a precisely measured obstruction that narrows the pipe and forces the
flowing fluid to constrict. The orifice plates are simple, cheap and can be delivered for almost any application in any material.
 |
| orifice plate |
uses
The Turndown rates for orifice plates are less than 5:1. Their accuracy are poor at low flow rates. A high accuracy depend on an orifice plate in good shape, with a sharp edge to the upstream side. Wear reduces the accuracy. Orifice, Nozzle and Ventury meter.







10 comments
commentsNice blog great information...
ReplyThanks for sharing...
Flow Meter, Humidity Meter, Countroller, Temperature Controller
This is Great Information, Nice blog...
ReplyThanks For Sharing...
Flow Meter, Temperature Logger, Tachometer, Temperature Controller
Great information, Thank you for sharing and keep posting.
ReplyGlovve professional Packers and Movers in India are leading movers and packers in India. we provide wide range of shifting services. Also, check -
Packers and Movers in Delhi
Packers and Movers in Mumbai
Packers and Movers Pune
Packers and Movers Hyderabad
Packers and Movers Bangalore
Packers and Movers in Chennai
Packers and Movers in Ahmedabad
Movers and Packers in Delhi
Movers and Packers in Mumbai
Movers and Packers in Pune
Movers and Packers in Hyderabad
Movers and Packers in Bangalore
Movers and Packers in Chennai
Movers and Packers in Ahmedabad
Impressive.. I loved this post.
Replycorrugated steel pipe
structural plate
CSP culvert
Great! thanks for sharing! since we are into the manufacturer of flow Meter, Process Industry Equipments Kindly have look at our products too!
ReplyThis is such an informative blog, your opinion, observations and ideas are amazing and to the point. I would love to read more content like this, and I want to give one advice to you are looking for a best builders in mp then Sagar Green Hills is the ideal township for you.
ReplyAs one of the most trusted Hydro testing services in UAE , we ensure your piping and systems are up to the task. Pressure Testing companies in UAE.
ReplyLooking for the best packers and movers service provided company in India. Then look no further than Packers and movers India.
ReplyPackers and movers in Vadodara
Packers and movers in Ahmedabad
Packers and movers in Hyderabad
Packers and movers in Bangalore
Packers and movers in Mumbai
Packers and movers in Delhi
Packers and movers in Jaipur
Packers and movers in Chennai
Amazing study blog
ReplyExam test |
Very good explanation!! While working myself with different survey instruments like Transit Theodolites , alignment telescope , Sight level , Total Station , Theodolites for couple of decades its quite refreshing
Reply